“Is ITC a Multibagger in the Making? Part -1

ITC is a diversified conglomerate with businesses spanning Foods, Personal Care, Cigarettes and Cigars, Education & Stationery Products, Incense Sticks and Safety Matches, Hotels, Paperboards and packaging, Agri business and Information Technology.
ITC was incorporated on August 24, 1910, under the name Imperial Tobacco Company of India Limited. The company name was later changed to India Tobacco Company Limited in 1970 and then to I.T.C limited in 1974.
ITC today has its presence across various countries and ITC’s omni-channel distribution infrastructure today reaches over 25 crore households in India.
But you’d be amazed to know that ITC was started in a leased office on the Radha Bazar Lane, in Kolkata. Starting off humble beginnings, ITC is behemoth today and each of its verticals requires extensive study. This is why we have divided this analysis into two parts.
Business Overview
- FMCG Cigarettes
- FMCG Others
- Agri-business
- Paperboards, Paper & Packaging
- Hotels
- Information Technology
FMCG Cigarettes: ITC is the leader in the organized domestic cigarette market with a market share of over 80%. It’s wide range of brands include Insignia, India Kings, Classic, Gold Flake, American Club, Wills Navy Cut, Players, Scissors, Capstan, Berkeley, Bristol, Flake, Silk Cut, Duke & Royal.
FMCG others: ITC has 25 mother brands spread across multiple FMCG sectors including:
- Packaged foods: Aashirvaad, Sunfeast, Bingo, Yippee noodles, Candyman and mint-o
- Personal Care: Savlon, Fiama, Vivel and Superia
- Stationary: Classmate and Paperkraft
- Agarbattis: Mangaldeep and AIM (matches)
‘ITC e-Store’, the Company’s exclusive D2C platform, is operational in 24,000+ pin-codes.
Agri-business: ITC is the second largest exporter of Agri products from the country. It trades in feed ingredients, food grains, marine products, processed fruits, coffee etc. It also exports leaf tobacco under this vertical. ITC is India’s largest and world’s 5th largest leaf tobacco exporter.
Paperboards, Paper & Packaging: ITC is the market leader in the value-added paperboards segment. It is also India’s largest converter of paperboard into high quality packaging. ITC manufactures the entire spectrum of paperboards – from 100% virgin, food-grade boards which are made from renewable and sustainable sources to 100% recycled boards.
Hotels: ITC entered into the Hotels business in 1975. ITC Hotels is one of the fastest growing hospitality chains in India and is the second-largest hotel chain in India, with 108 hotels in 70 locations. It possesses an inventory of ~290,000 rooms. ITC hotels are classified under 4 distinctive brands:
- ITC Hotels
- Welcomhotels
- Fortune Hotels
- Welcom Heritage.
IT: ITC Infotech is a leading global technology services and solutions provider, led by Business and Technology Consulting. The company provides technology solutions and services to enterprises across industries such as Banking & Financial Services, Healthcare, Manufacturing, Consumer Goods, Travel and Hospitality.
Revenue Breakdown:
The segmental revenue breakdown is as per the Q4 FY24 report:
The overall revenue for Q4 FY24, is INR 19,297 crore of which:
- Cigarettes contributed INR 7,925 crore & 41.1 of the revenue.
- Other FMCG contributed INR 5,300 crore & 27.5% of the revenue.
- Hotels contributed INR 898 crore & 4.7% of the revenue.
- Agri Business contributed INR 3,101 crore & 16.1% of the revenue.
- Paper Board business contributed INR 2,073 crore & 10.7% of the revenue.
Industry Overview: Cigarettes – Tobacco
Globally, cigarettes are the most common form of tobacco use. However, in India, tobacco consumption takes on many different forms, including various chewing and smoking options available across price ranges. This diversity stems largely from the heavy and unequal taxation imposed on cigarettes. While India is the second-largest consumer of tobacco worldwide, legal cigarettes account for just 9% of the country’s total tobacco use, compared to a global average of 90%. Despite having 18% of the world’s population, India makes up less than 2% of global cigarette consumption, resulting in one of the lowest per capita cigarettes use rates globally.
Over time, steep and discriminatory taxes on cigarettes have driven consumers toward lower-taxed or untaxed tobacco products, such as illicit cigarettes, bidis, and chewing tobacco (Gutkha, Zarda etc.). Although legal cigarettes’ share of total tobacco consumption has dropped from 21% in 1981-82 to just 9% today, the overall use of tobacco in India has increased. Despite representing less than 10% of total tobacco consumption, legal cigarettes generate over 80% of the revenue from the tobacco sector.
Cigarette taxes in India are significantly higher than in developed nations, being 14 times greater than those in the U.S., 7 times higher than in Japan, and 6 times more than in Germany. Additionally, India’s cigarette taxes are much steeper compared to neighboring countries as well.
Competition Intensity:
To understand the competition intensity in the Tobacco industry, we need to explore the different types of tobacco which are available in the market. India with its rich agro-climatic diversity has the unique position of growing all types of tobacco which are broadly classified as:
- FCV Tobacco
- Bidi Tobacco
- Cigar & Cheroot
- Hookah Tobacco
- Chewing & Snuff
- Natu, Burley, Lanka & HDBRG
- Pikka Tobacco
In India, cigarettes are manufactured largely using Flue Cured Virginia (FCV) tobacco grown in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Karnataka.
The Indian cigarette market is dominated by four companies: ITC Limited, Godrey Philips India Limited (GPI), VST Industries Ltd, Philip Morris International.
ITC had a market share of over 73% in 2022. Godrey Philips India Limited (GPI) had a market share of almost 10% in 2022 and VST had a market share of over 9% in 2022.
ITC position in this segment:
Market leader in tobacco: ITC is the market leader in the tobacco business. In 2022, ITC had a market share of 78%.
- ITC is the market leader in cigarettes in India. With a portfolio of invaluable brands, ITC’s cigarette business stands testimony to the company’s quality, innovation and consumer focus.
- More than one hundred years of expertise in developing products to match the evolving taste of consumers has led to a portfolio of very strong brands.
- The company has five cigarette manufacturing factories across India in Bengaluru, Kolkata, Munger, Pune, and Saharanpur.
Risks:
- High reliance on Tobacco revenues: ITC is heavily reliant on its cigarette business for its revenue. Although it has tried to diversify its FMCG segment, cigarettes still account for around 40% of revenues and about 81% of operating income.
- As of FY 2024, the FMCG – Cigarettes contributed INR 30,596 crore.
- Any impact on the overall business of the Tobacco industry will impact the overall finances of the company.
- High taxes: Taxes on cigarettes remain one of the highest in India as depicted in the chart:
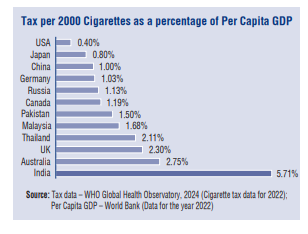
Huge taxes on the legal cigarette industry in earlier years have resulted in rapid growth of illicit cigarette trade – making India the 4th largest illicit cigarette market globally according to Euromonitor estimates.
- Rise of Illicit cigarettes: Over the years, discriminatory and punitive taxation on cigarettes has led to progressive migration of consumption from duty-paid cigarettes to other lightly taxed/tax-evaded forms of tobacco products, comprising illicit cigarettes, bidi, chewing tobacco, gutkha, zarda, snuff, etc. It is pertinent to note that while the share of legal cigarettes in total tobacco consumption has declined from 21% in 1981-82 to a mere 9%, aggregate tobacco consumption in the country has increased over the same period. As a result, despite accounting for less than 1/10th of the tobacco consumed in the country, duty-paid cigarettes contribute more than 4/5th of the revenue generated from the tobacco sector.
- Regulatory Risks: The government imposes stringent rules on cigarette marketing, with complete bans on advertising through traditional media. Additionally, the Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA) mandates large pictorial warnings on cigarette packs and strict packaging norms. Any further tightening of these regulations could impact ITC’s ability to promote its products and maintain its market share.
Hotels Industry Overview
The global Travel & Tourism industry, which had been severely impacted during the pandemic, has witnessed a strong rebound in the last two years. According to estimates of the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC), the Travel & Tourism sector is expected to contribute US$ 9.9 trillion to the global economy in 2023 (about 96% of pre-pandemic levels).
The hospitality industry is a vital component of the tourism industry and plays a crucial role in earning foreign exchange, contributing to revenue generation, and job opportunities in the host community. The hotel industry is highly dependent on the tourism industry as a source of revenue, and ministries such as tourism, railways, and civil aviation play a significant role in the growth.
So, before going further we need to discuss the operating models of hotels. There are two popular models:
The Asset-Light and Asset-Right models are strategic approaches used by hotel chains and other service-oriented businesses to optimize their operations and financial performance while minimizing capital investment.
Asset-Light Model
In the Asset-Light model, hotel companies prioritize running and managing properties rather than owning the underlying real estate.
Asset-Right Model
The Asset-Right model is a more tailored approach, where a company combines asset-light principles with selective ownership of key properties that are strategically important.
This is the basic overview of the Hotel Industry.
ITC position in this segment:
Strengths:
- Diversified Hotel chain: ITC Hotels is one of the largest hotel chains in the world with over 130 properties across more than 80 destinations. ITC’s Hotels Business continues to leverage its ‘asset-right’ strategy to be amongst the fastest growing hospitality chains in the country with over 130 properties and 12,000 rooms under distinctive brands – ‘ITC Hotels’ in the Luxury segment, ‘Mementos’ in the Luxury Lifestyle segment, ‘Welcomhotel’ in the Upscale segment, ‘Storii’ in the Boutique Premium segment, ‘Fortune’ in the Mid-market to Upscale segment and ‘WelcomHeritage’ in the Leisure & Heritage segment.
Industry Overview of Paperboards, Paper & Packaging:
The Indian paper industry is highly fragmented. It comprises of small, medium and large paper mills with paper production capacity ranging from 10 to 1,650 tonnes per day.
The paper industry in India produces 5 percent of the world’s total paper. India accounts for about 5 percent of the global paper market. The market is worth about US $8 billion. The paper industry in India generated an estimated INR 70,000 crore in yearly revenue, with a domestic market size of INR 80,000 crore. The paper industry’s tax contribution to the Government is around INR 5,000 crore.
In India, per capita consumption of paper is about 15-16 kg, which is much lower than the world average of 57 kg.
Strong favorable demographics, increasing disposable income levels, rising consumer awareness and demand for processed food have been the prime factors behind the surge in demand of plastic packaging.
ITC Position in this segment:
- Integrated pulp and paper mill: ITC Established India’s largest integrated pulp and paper mill, anchoring inclusive fiber value chain. The Classmate and Paperkraft range of notebooks leverage the company’s world-class fibre line at Bhadrachalam, also India’s first ozone treated elemental chlorine free facility.
- Strong brand for Books segment: ITC’s popular range of Education & Stationery Products includes notebooks, pens, pencils, art stationery, geometry boxes & scholastic products, premium notebooks and notepads under the brands ‘Classmate’ and ‘Paperkraft’.
- Decline in Paperboards segment revenues: – Revenues declined by 7% YoY, and EBIT declined 34% YoY owing to subdued domestic demand and increased competitive intensity from cheap Chinese players. Margins were largely impacted on the back of negative operating leverage and increased input cost.
So far, we have discussed ITC’s three lines of business, namely Tobacco, Hotels and Paper & Packaging. As we already know, there are two more business lines that ITC operate in, which are Agri-business & several FMCG products.
You must be wondering why this conglomerate is operating in such varied sectors? What is the co-relation between all these business lines?
In the next part of ITC’s stock analysis video, we will go into the depth of ITC’s Agri & FMCG businesses, and how all the business lines at ITC are inter-connected. We will also be discussing the Company’s overall financials, shareholding patterns, ESG and several other fundamentals based on which you can decide whether ITC is a good pick for investing.

Discussions